Visual Effects
Using nerfies you can create fun visual effects. This Dolly zoom effect would be impossible without nerfies since it would require going through a wall.
The goal of Arbitrary Style Transfer (AST) is injecting the artistic features of a style reference into a given image/video. Existing methods usually pursue the balance between style and content by adjusting general coarse-level stylized strength, thereby leading to unsatisfactory results and hindering their practical application. To address this critical issue, a novel AST approach namely Flexibly Controllable Arbitrary Style Transfer (FAST) is proposed, which is capable of explicitly customizing the stylization results according to various source of semantic clues. In the specific, our model is constructed based on Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) and elaborately designed to absorb content and style instance as conditions of LDM. It is characterized by introducing of Style-Adapter, which allows users to flexibly manipulate the stylization results via aligning multi-level style control information and intrinsic knowledge in LDM, meanwhile enhancing the model with improved capacity to harmonize content detail retention and stylization strength. Lastly, our model is extended to handle video AST task. A novel learning objective is leveraged for video diffusion model training, which considerably improve cross-frame temporal consistency on the premise of maintaining stylization strength. Qualitative and quantitative comparisons as well as user studies demonstrate our presented approach outperforms the existing SoTA methods in generating visually plausible stylization results. The project homepage for the paper is available at: https://fast-ldm.github.io/.
Using nerfies you can create fun visual effects. This Dolly zoom effect would be impossible without nerfies since it would require going through a wall.
As a byproduct of our method, we can also solve the matting problem by ignoring samples that fall outside of a bounding box during rendering.
We can also animate the scene by interpolating the deformation latent codes of two input frames. Use the slider here to linearly interpolate between the left frame and the right frame.
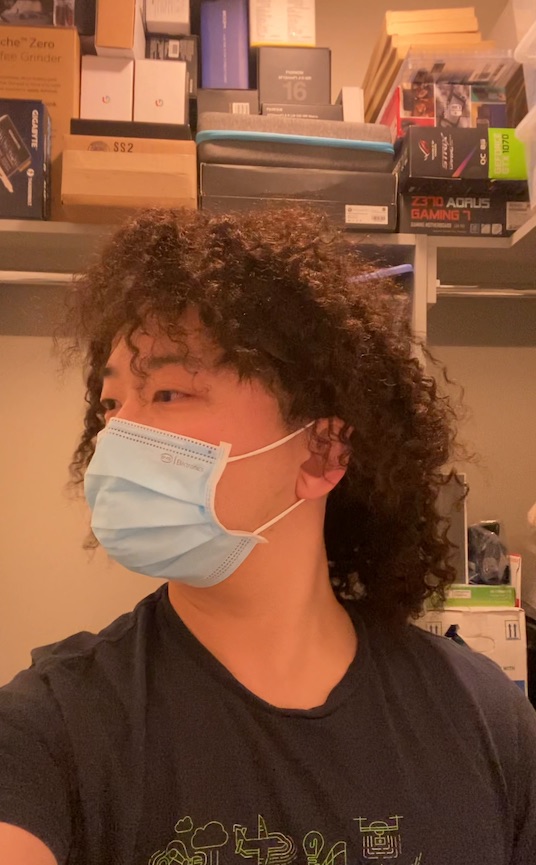
Start Frame
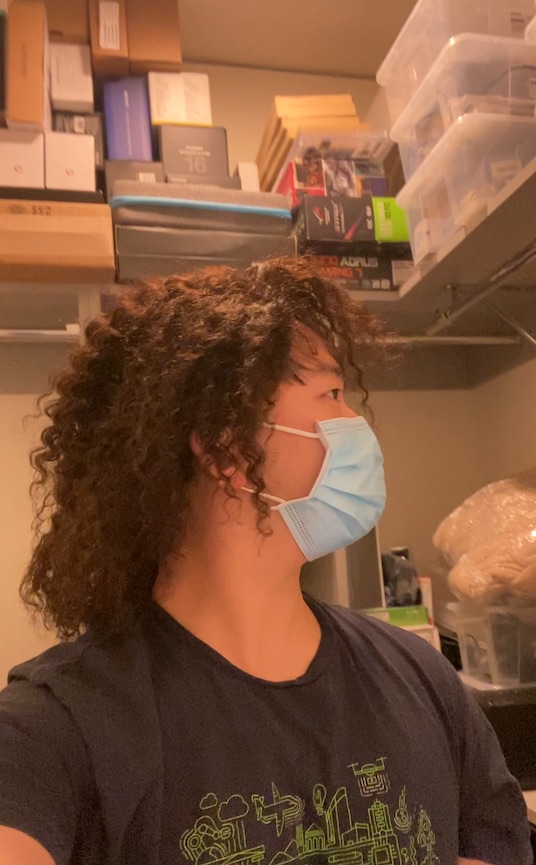
End Frame
Using Nerfies, you can re-render a video from a novel viewpoint such as a stabilized camera by playing back the training deformations.
There's a lot of excellent work that was introduced around the same time as ours.
Progressive Encoding for Neural Optimization introduces an idea similar to our windowed position encoding for coarse-to-fine optimization.
D-NeRF and NR-NeRF both use deformation fields to model non-rigid scenes.
Some works model videos with a NeRF by directly modulating the density, such as Video-NeRF, NSFF, and DyNeRF
There are probably many more by the time you are reading this. Check out Frank Dellart's survey on recent NeRF papers, and Yen-Chen Lin's curated list of NeRF papers.
@article{wang2025fast,
title={FAST: Flexibly Controllable Arbitrary Style Transfer via Latent Diffusion models},
author={Wang, Hanzhang and Wang, Haoran and Yu, Zhongrui and Sun, Mingming and Jiang, Junjun and Liu, Xianming and Zhai, Deming},
journal={ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications},
publisher={ACM New York, NY},
year={2025},
}